Types of Yarn
There are a wide variety of fibers that are used to create yarns that you can use for knitting and crocheting and they come from a variety of sources. Yarns are made from a group of fibers twisted together to form a continuous strand. The fibers used to create these yarns include animal fibers, plant fibers and synthetic fibers. There are benefits and negatives for each type of fiber and yarn, but with such a wide variety you’re sure to find the perfect fit for your project.
Animal fiber based yarns include Alpaca, Angora, Cashmere, Silk and Sheep wool.
Alpaca Fiber

Alpaca fiber is similar to sheep's wool and is another natural, animal fiber. It's harvested from Alpaca's and while similar to sheep's wool, does have different characteristics. It contains no lanolin making it hypoallergenic and it's warmer than sheep's wool. Alpaca yarn was first used in the early 1800's in England though it took some effort for it to become a workable material. This was because the yarn was being woven into a cam-let type fabric which didn't work well with the alpaca yarn. Once the warp and weft method was introduced, alpaca yarn was able to be woven into a successful fabric.
Product Qualities:
Strength per same fineness.
Warmth per weight. Approx. 3x the insulating capacity of sheep’s wool, so garments are VERY light and VERY warm.
Hypoallergenic. Incidence of allergic reactions is dramatically lower than other fibers.
Feel. Has no lanolin and very low “prickle factor” thus is softer, less irritating!
There is less shrinkage and has a superior comfort, and superior comfort range.
Yield – As soft and fine as cashmere. 7 – 10lbs of fiber yearly yield vs a cashmere goat yield of 2-3lbs. alpaca will yield 10lbs of fiber a year.
Colors in herd. There are 23 recognized natural colors which accept both natural plant based and acid dyes.
Environmental impacts:
Due to their padded feet Alpaca's don't trample or damage the ground in large herds allowing more grass and plants to grow with the herd. While Alpaca's only eat 1.5% of their body weight you can feed more Alpaca with the same amount of food a sheep herd would take. Not only that but when Alpaca eat vegetation they only eat the leaves or fruit or stem and never the roots as they want to come back and eat it again; unlike sheeps or goats who do eat a plant roots and all. Allowing for again a continuing growth of vegetation within the herd. While they also poop in one location as a communal bathroom their poop makes wonderful organic fertilizer with minimal if any processing.
Sheep's Wool

There are a few different varieties of sheep's wool depending on the breed of the sheep the wool is coming from. The two most common types of sheep's wool are merino and lopi with merino being the most common and prized type of sheep's wool.
Product Qualities:
They are composed of amino acids.
They have excellent absorbency.
Moisture regain is high.
They tend to be warmer than others.
They have poor resistance to alkalis but good resistance to acids.
They have good elasticity and resiliency.
Environmental Impacts:
Sheep are known as the humvee's of the animal kingdom. As they eat mass amounts of food and provide as much methane pr animal as a cow does. Being one of the massive contributors to greenhouse gasses over the last 250 years. As well as sheep farms have one of the worst wraps towards animal cruelty due to their horrific treatment of the sheep.
Silk from Silkworms

Silk is produce by insect larvae so that they can form cocoons. Bombyx mori, also known as Mulberry silkworms, produce the most widely known form of silk but for textile manufacturing, moth caterpillars are generally the one type used.
Product Qualities:
Silk has a liability and suppleness that, aided by its elasticity and resilience, gives it excellent drapability. Silk fabrics retain their shape and have moderate resistance to wrinkling. Fabrics that are made from short – staple spun silk have less resilience. Silk is a protein fibre and is a non-conductor of heat similar to that of wool. This makes silk suitable for winter apparel.
Environmental impacts:
According to "Environmental Impact. (n.d.). Retrieved August 21, 2020, from https://globalcommodities-silk.weebly.com/environmental-impact.html"; the impact of the silk industry is primarily that of the fact the two main types of silk worm used are not capable of living outside of captivity. Further more almost all silk comes form China and India requiring mass amounts of transportation globally to acquire silk.
Angora Fiber
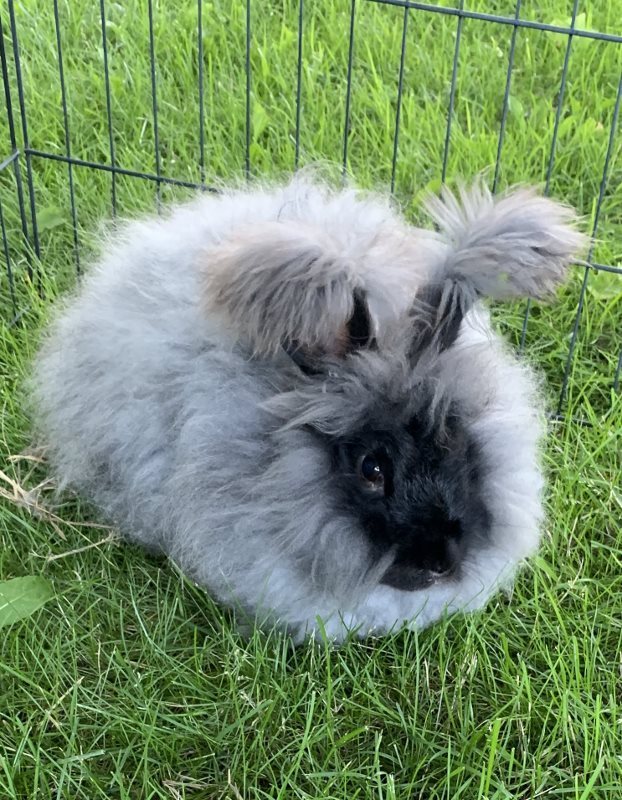

Angora hair/fiber comes from the coat of the angora rabbit. Being similar to cashmere, mohair, and silk it is sought after for its light and thinness by knitters.
Product Qualities
Angora fiber is incredibly light as it has a hollow core. Also with it being able to retain heat well it is warmer than wool fibers. Also has a unique halo ability which is its fluffiness.
Environmental Impacts
According to "Mari, A. (2020, July 03). The Life Impact of Angora Wool [Fabric, Material, Textile Guide for Health, Animals, Environment]. Retrieved August 21, 2020, from https://healabel.com/a-fabrics-materials-textiles/angora-wool"; angora wool is incredibly unethical towards to angora rabbits. While it also requires mass amounts of destructive chemicals to dye or bleach angora fiber causing severe harm to nearby ground water.
Cashmere

Cashmere is wool from the cashmere or pashmina goats. Being used to make yarn and textiles for hundreds of years. Still mainly being produced in china and Mongolia there are a few spots around the globe able to care for or process cashmere.
Product Qualities
Cashmere is antibacterial meaning its great for sports wear as it doesn't smell after usage; as well as being a more breathable fiber than synthetics. Cashmere is also biodegradable allowing for easier waste disposal. provides lofted insulation.
Environmental Impacts
Due to the hooves of the goats feet their damage ground and as their herds grow larger the damage to the ground becomes unable to grow life. While 90% of all cashmere comes from china and Mongolia; thus meaning their is large transportation involved to get the wool to plants and factories.
Plant fiber based yarns include hemp, cotton and bamboo.
Hemp

Hemp fiber has been a commonly used fiber for centuries. In addition to yarn, hemp fibers can be used for fabrics and textiles, rope, and even food. Hemp has a great deal of benefits as it can grow much more quickly than trees and requires less water and no pesticides or fertilizers.
Product Qualities
Three times stronger than cotton
Good abrasion resistance/very durable
Anti-microbial and UV resistance
Naturally resistant to mold, mildew, rot
Readily takes dyes
Softens with each washing, without fiber degradation
Breathable
Washable or dry cleanable
Environmental Impacts
Hemp offers many different uses that can promote a more sustainable world. Hemp products can be recycled, reused and are 100% biodegradable. Proponents of hemp claim that it can help reduce global warming because it takes out large amounts of carbon dioxide per acre, more than most plants.
Cotton

Cotton is a very popular source for thread and textile manufacturing with a variety of types that can be grown and used. The 3 most popular types of cotton used for yarn manufacturing are Egyptian cotton, Pima cotton and American cotton. Each have their own benefits over the other. Egyptian cotton is the longest cotton fiber and is softer than the other types of cotton. American cotton is available the widest amount of colors thanks to it being able to take dye better than other types of cotton. Pima cotton is a mixture between Egyptian and American cotton with properties of both.
Product Qualities
Cotton fibers are natural hollow fibers; they are soft, cool, known as breathable fibers and absorbent. Cotton fibers can hold water 24–27 times their own weight. They are strong, dye absorbent and can stand up against abrasion wear and high temperature.
Environmental Impacts
Cotton’s most prominent environmental impacts result from the use of agrochemicals (especially pesticides), the consumption of water, and the conversion of habitat to agricultural use. Diversion of water and its pollution by cotton growing has had severe impacts on major ecosystems such as the Aral Sea in Central Asia, the Indus Delta in Pakistan and the Murray Darling River in Australia.
Bamboo

Bamboo fibers are generally too short to be used to create a natural fiber, but bamboo bast can be used in combination with a chemical process to create rayon which is synthetic fiber. The environmental benefits of bamboo still are valid as they can be harvested without killing the plant, are a carbon sink, they produce oxygen and they control soil erosion. The main environmental benefit of bamboo is that it can grow and spread quickly without much use of water, pesticides or fertilizers.
Product Qualities
Softer than cotton, with a texture similar to a blend of cashmere and silk. Because the cross-section of the fibre is filled with various micro-gaps and micro-holes, it has much better moisture absorption and ventilation. Moisture absorbency is twice than that of cotton with extraordinary soil release. Natural antibacterial elements
Environmental Impacts
Processing bamboo into fiber requires intense chemical processing. The bleaching process usually follows the conventional method of bleaching, which involves harmful heavy metal pollutants. The post-bleach phase involves processing the wood pulp with acid, generating emissions to air of sulphur, nitrous oxide, carbon disulphide and hydrogen sulphide, all harmful air pollutants. This chemical processing, which is highly water intensive, results in water discharge that is also highly polluting if released untreatedP
Synthetic fiber base yarns include nylon, polyester and rayon.

Synthetic fibers are commonly used to create yarn because they're durable than most natural fibers and they can be easily dyed different colors. There are other popular benefits such as stain resistance, water proofing and stretching that lead many to choose a synthetic fiber over a natural fiber.
Rayon

Rayon is a manufactured cellulose fiber that is commonly made from purified cellulose from wood and plant pulp. Even though the process starts with a wood or plant pulp, the chemical process that it goes through makes a semi-synthetic fiber with no identifiable properties of the original natural fiber. There are a variety of methods used to create rayon. There is the acetate method with involves the reaction with ceullose and acetic anyhydride which forms cellulose acetate. The resulting fiber can be used to create cigarette filters and playing cards. There is also the cuprammonium method which involves combining cellulose with copper and ammonia to make the cellulose a soluble compound. The resulting fiber from this process is very fine and has a silk feel to it and is commonly used in sundresses and blouses. The most popular method to create rayon fibers is the viscose method. This method was created to create an artificial silk. These days many types of natural fibers that can be used to start this process such as hemp pulp or bamboo pulp. Even though these fibers are used in the process, the final product can't be considered a natural product due to the chemical process that is involved. After viscosity the original fibers used can't even be identified. Rayon and viscose are interchangeable terms within the US and both can be used to label the same final product.
Product Qualities
Rayon fabrics are soft, smooth, cool, comfortable, and highly absorbent, but they do not always insulate body heat, making them ideal for use in hot and humid climates, although also making their "hand" (feel) cool and sometimes almost slimy to the touch.
Environmental Impacts
Rayon is made from plants, but it's not eco-friendly because of its toxic production and the deforestation associated with it.
Nylon

Nylon is a very popular synthetic fiber that first was used in 1935. It is commonly used for clothing, namely women's stockings, but can also be used for car parts, electrical equipment and food packaging films. Nylon was created to be a synthetic replacement for silk due to silk becoming scarce during World War II. It was used to manufacturer parachutes, flak vests and vehicle tires.
Product Qualities
Nylon fibers are exceptionally strong and elastic and stronger than polyester fibers. The fibers have excellent toughness, abrasion resistance, and are easy to wash, and to dye in a wide range of colors. The filament yarns provide a smooth, soft, and lightweight fabric of high resilience.
Environmental Impacts
Greenhouse gases: producing nylon creates nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas that is 300 times more potent than carbon dioxide. Water: manufacturing nylon is a very thirsty process; large amounts of water are used for cooling the fibers, which can be a source of environmental contamination and pollution.
Polyester

Polyester is another popular type of synthetic fiber and it is mostly used in clothing. Polyester is a category of polymer that includes natural chemicals such as the cutin in plant cuticles and synethetic chemicals. Natural based polyesters are biodegradable but most synthetic ones are not. Polyester thread can be used to create fabrics that are used in clothing, furniture and linens and even items such a mousepads. Polyester can also be blended with natural fibers such as cotton which can change the properties of the resulting material. Blended with cotton, polycotton is tear and wrinkle resistant and strong. It also helps reduce shrinking.
Product Qualities
Polyester is very durable and resistant to many chemicals. It is resistant to shrinking, stretching, wrinkling, and abrasions. The fibers used to create polyester are very strong yet lightweight
Environmental Impacts
Requires more than double the energy of conventional cotton to produce. The production of polyester uses harmful chemicals, including carcinogens, and if emitted to water and air untreated, can cause significant environmental damage. Most polyester is produced in countries such as China, Indonesia and Bangladesh where environmental regulations are lax, and air and water pollution is often discharged untreated, resulting in significant pollution and harm to communities in the vicinity